Corporate Travel Booking System Streamlined Solutions
A corporate travel booking system is crucial for modern businesses. It streamlines the often-complex process of arranging trips for employees, from flights and hotels to car rentals and expense reports. A well-designed system can significantly improve efficiency and reduce administrative burden, ultimately saving valuable time and resources. This system can integrate seamlessly with existing corporate tools, providing a holistic approach to travel management.
This overview explores the key features, user experience, and integration aspects of a modern corporate travel booking system. We will delve into functionalities like flight, hotel, and car rental booking, alongside comprehensive expense report management and travel policy administration. Furthermore, we will examine the importance of intuitive user interfaces and secure data management within the system.
System Features and Functionality
A modern corporate travel booking system streamlines the often complex process of arranging business trips, significantly improving efficiency and reducing administrative overhead. These systems provide a centralized platform for managing all travel-related activities, from initial booking to expense reporting. This detailed overview highlights the core features and functionalities of such a system.
The key objective of a corporate travel booking system is to optimize travel arrangements while simultaneously adhering to company policies and controlling expenses. This is achieved by integrating various booking functionalities, managing travel policies, and seamlessly integrating with existing corporate tools.
Core Booking Functionalities
A robust system offers a unified interface for booking flights, hotels, and car rentals. This centralized approach simplifies the process for employees and travel administrators alike. Users can search and compare options across multiple providers, selecting the best fit based on price, availability, and preferred travel class. For instance, the system could allow for filtering by specific airlines, hotel chains, or car rental agencies, enabling a more targeted search.
Flight Booking
This feature allows users to search for flights based on various criteria, including departure and arrival cities, dates, and preferred airlines. The system can display flight details, including flight number, duration, layover information, and associated costs. Integration with airline loyalty programs allows employees to earn points during business travel. Real-world examples include large corporations leveraging the system to book flights for thousands of employees annually.
Hotel Booking
Users can search and book hotels based on location, dates, and specific amenities. The system provides detailed information about each hotel, including room types, pricing, and customer reviews. The system could also allow users to pre-select preferred hotel chains, or integrate with loyalty programs. An example of this is a company utilizing the system to book hotel rooms for a large conference, ensuring all attendees have comfortable accommodations.
Car Rental Booking
This functionality facilitates the booking of car rentals. Users can select from a variety of car types, specify the rental duration, and choose pick-up and drop-off locations. The system displays pricing information and allows for the comparison of options from different rental companies. A notable use case is a company that regularly requires cars for business trips across multiple regions.
Travel Policy Management
The system allows for the creation and management of company-wide travel policies, ensuring compliance with regulations and cost-effectiveness. These policies can define permissible expenses, preferred travel classes, and other relevant restrictions. For example, the system might require pre-approval for certain travel arrangements exceeding a specified budget.
Expense Reporting
The system facilitates the submission and approval of expense reports. Employees can easily input travel expenses, including receipts, mileage, and other relevant details. The system then verifies compliance with travel policies and ensures accurate accounting. This process streamlines the expense reporting procedure for businesses.
Integration with Corporate Tools
The system can integrate with other corporate tools, such as calendar applications, project management software, and accounting systems. This seamless integration enhances the overall workflow and data consistency. For instance, bookings can be automatically synchronized with calendars, ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of travel arrangements.
Travel Booking Options
| Travel Type | Features |
|---|---|
| Business | Supports pre-approval workflows, expense tracking, and integration with project management tools. |
| Personal | Provides a separate booking area for employees to manage personal travel, but may have restrictions based on company policy. |
| Conference/Event | Facilitates group booking, hotel block reservation, and potentially catering/other event-related management. |
| Other | Offers flexibility for miscellaneous travel needs that may not fit neatly into the business or personal categories. |
User Experience and Interface

Source: itilite.com
A user-friendly interface is paramount for a corporate travel booking system. A seamless experience reduces friction, leading to faster bookings and potentially lower administrative costs. Well-designed interfaces improve employee satisfaction and streamline the entire travel process.
Intuitive interfaces, coupled with efficient data presentation, empower employees to make informed decisions, ultimately saving time and resources. Clear and consistent design choices foster a positive user experience, improving the overall effectiveness of the system.
Impact of User-Friendly Interfaces on Booking Efficiency
Effective interfaces directly influence the efficiency of corporate travel bookings. A streamlined system allows employees to quickly find relevant information, select suitable options, and complete bookings with minimal effort. This efficiency translates into time savings for both employees and the travel department, contributing to a more productive workflow.
Best Practices for Intuitive Dashboards and Navigation Menus
Clear and consistent design principles are essential for intuitive dashboards and navigation menus. The consistent use of visual cues, such as colors and icons, enhances recognition and reduces the learning curve. Employing a logical hierarchical structure for navigation menus allows users to easily locate specific functionalities. Dashboards should be personalized to provide relevant information at a glance, focusing on key metrics and recent bookings. Avoid cluttering the interface with unnecessary information; instead, prioritize key data points for easy comprehension.
Comparison of Interface Designs
Different interface designs cater to various user needs and preferences. A mobile-first approach prioritizes the mobile experience, ensuring a seamless booking process across all devices. Desktop-focused interfaces might offer more comprehensive features and advanced functionalities but could lack the responsiveness needed for mobile users.
| Interface Design | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile-first | Excellent responsiveness across devices, convenient on-the-go access, often simpler and easier to navigate on smaller screens. | Limited space for complex functionalities may require compromises in feature sets for mobile users. |
| Desktop-focused | Offers more comprehensive features and customization options, greater flexibility for complex tasks. It may | y may not be as user-friendly on mobile devices, potentially less intuitive for less experienced users. |
Importance of Accessibility Features
Accessibility features are crucial for ensuring inclusivity and equal access to the system for all users. Designing with accessibility in mind benefits everyone, including users with disabilities. Features like adjustable font sizes, keyboard navigation, and alternative text for images are essential for a comprehensive and inclusive user experience. Adherence to accessibility guidelines ensures compliance with regulations and fosters a more welcoming environment for all employees.
Effective Presentation of Complex Data
Presenting complex data in a user-friendly manner is essential for facilitating informed decision-making. Employing interactive charts and graphs allows users to visualize trends and patterns quickly. Using color-coding and highlighting key metrics can enhance comprehension and make data analysis more intuitive. Providing clear labels and explanations alongside visualizations minimizes the need for extensive training and ensures users can grasp the significance of the presented data quickly. Data should be presented in a clear, concise, and easy-to-understand format.
Integration and Data Management: Corporate Travel Booking System
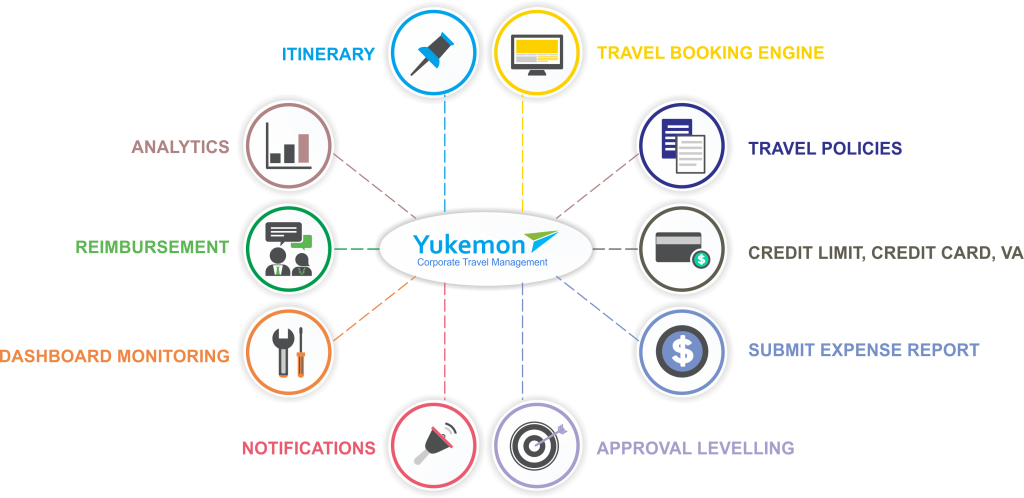
This section details the crucial aspects of integrating the travel booking system with existing corporate systems, ensuring data security and privacy, and outlining data management strategies. Proper integration minimizes disruptions, maximizes efficiency, and maintains data integrity throughout the system.
The system’s architecture is designed to seamlessly integrate with diverse corporate environments. Data management procedures are rigorously implemented to maintain confidentiality and compliance with relevant regulations.
Integration Methods, Corporate travel booking system
Various methods facilitate integration with existing corporate systems, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Selecting the appropriate method depends on the specific requirements of the corporate environment and the existing infrastructure.
- API Integration: Utilizing Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allows for direct communication between the travel booking system and other applications. This approach offers flexibility and scalability, enabling real-time data exchange. APIs are often favored for their ability to integrate with diverse software, facilitating streamlined data flow between different systems. For example, connecting to a company’s expense reporting system via API allows automatic expense claim processing.
- Middleware Integration: Middleware acts as a bridge between different systems, facilitating communication and data exchange. This approach is particularly beneficial for systems that lack standardized APIs or use different communication protocols. Middleware often handles data translation and format conversions, making integration smoother for various systems. This method offers a centralized point for managing data transfers between the travel booking system and other applications.
- Custom Integration: Custom integration involves developing specialized code to connect the travel booking system with existing systems. This approach offers maximum customization, tailoring the integration to specific business needs. However, it often requires significant development resources and time. This method is ideal for organizations with complex, non-standard systems. For example, integrating with a legacy system that lacks modern APIs necessitates custom code for data transfer.
Data Security and Privacy
Robust security measures are essential to safeguard sensitive traveler data. The system adheres to industry best practices and relevant data privacy regulations.
- Data Encryption: All data transmitted and stored within the system is encrypted using industry-standard protocols to protect against unauthorized access. This ensures the confidentiality and integrity of traveler data.
- Access Control: Role-based access controls restrict data access to authorized personnel, preventing unauthorized modifications or viewing of sensitive information. This method ensures only authorized personnel can access specific data elements.
- Compliance: The system complies with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, to ensure the protection of personal information.
Data Points Collected and Stored
The system collects and stores various data points to facilitate efficient travel bookings and reporting. These data points are categorized and organized for comprehensive analysis.
- Traveler Information: This includes details such as name, contact information, travel preferences, and loyalty program memberships. This ensures accurate and efficient travel arrangements.
- Booking Details: Information about flights, hotels, rental cars, and other travel arrangements is meticulously documented for easy reference and reporting. These details are crucial for tracking and analyzing travel expenses.
- Financial Transactions: Details about payments made for bookings, including payment method and transaction history, are stored securely. This enables detailed financial tracking and reporting.
- System Usage: Detailed records of system usage, including login attempts, access times, and actions taken, are stored to assist with auditing and troubleshooting. This detailed audit trail enhances security and helps identify potential issues.
Integration Methods Comparison
A table summarizing various integration methods and their respective advantages and disadvantages:
| Integration Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| API Integration | Flexibility, Scalability, Real-time Data Exchange | Requires API documentation and support, Potential complexity for complex systems |
| Middleware Integration | Handles data translation, Centralized management | Can introduce latency, potentially higher cost than API integration |
| Custom Integration | Maximum customization, tailored to specific needs | High development cost, Time-consuming, Potential for security vulnerabilities |
Data Backup and Recovery
Robust data backup and recovery procedures are crucial for maintaining business continuity and data integrity. Regular backups ensure data availability in case of system failure or data loss.
- Regular Backups: Scheduled backups are performed to safeguard data against accidental deletion or corruption. This process involves regularly backing up data to a secure offsite location. For example, nightly backups to a cloud storage service protect against local hardware failure.
- Redundancy: Data redundancy ensures data availability even if one system component fails. This ensures data availability in case of unexpected system failures.
- Disaster Recovery Plan: A comprehensive disaster recovery plan Artikels procedures for restoring data and systems in case of a major incident. This includes detailed steps for restoring data and systems from backups.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, a robust corporate travel booking system offers significant advantages for businesses. It optimizes the travel process, enhances user experience, and seamlessly integrates with existing corporate tools. By streamlining booking procedures, managing expenses effectively, and prioritizing user-friendly interfaces, companies can enhance employee satisfaction and operational efficiency. This approach not only reduces administrative burdens but also fosters a more organized and productive work environment.