Pleasant Agent A User-Focused Approach
Pleasant agent sets the stage for a detailed exploration of designing and implementing user-centric agents. This exploration dives into the core principles of creating positive interactions, encompassing everything from defining agent characteristics to crafting effective communication strategies. It covers a wide spectrum, from virtual assistants to customer service representatives, highlighting the key elements that contribute to a positive user experience.
The content delves into the attributes and behaviors of pleasant agents, examining how tone, language, and empathy influence user perception. It then explores the crucial role of interaction design in achieving these pleasant interactions, showcasing examples in diverse scenarios. The discussion also touches upon training methodologies, measurement techniques, and the future of pleasant agents in various contexts, like customer service and entertainment.
Defining Pleasant Agent

A pleasant agent is more than just a helpful tool; it’s an experience. It’s designed to interact with users in a way that fosters positive feelings and a smooth, efficient process. This involves understanding user needs, anticipating potential issues, and delivering solutions in a manner that is not only helpful but also considerate and engaging.
Pleasant agents are not simply robots; they are designed to mimic human interaction in a way that builds trust and rapport. Their purpose extends beyond mere task completion to encompass a positive emotional connection with the user. This positive interaction leads to a higher level of user satisfaction and, ultimately, a more successful interaction.
Characteristics of a Pleasant Agent
Pleasant agents possess a range of characteristics that contribute to a positive user experience. These characteristics go beyond basic functionality to encompass a more human-like interaction. Empathy, understanding, and a proactive approach are critical components.
- Empathy: Pleasant agents demonstrate an ability to understand and respond to user emotions, recognizing nuances in tone and context. This might involve acknowledging frustration or offering encouragement, fostering a sense of connection and support.
- Understanding: Beyond simply responding to specific s, pleasant agents demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the user’s needs and goals. They proactively anticipate needs, providing relevant information and solutions before the user explicitly requests them.
- Proactive Approach: Pleasant agents do not wait for the user to initiate interaction. They anticipate user needs and offer assistance where appropriate. This could involve offering relevant information, suggesting alternative solutions, or gently guiding the user toward the desired outcome.
- Clear and Concise Communication: Pleasant agents use clear, concise language that is easy to understand. They avoid jargon or overly technical terms, ensuring that the user feels comfortable and confident in their interaction.
- Patience and Tolerance: Pleasant agents maintain a calm and patient demeanor, even in challenging situations. They handle user frustration with grace and professionalism, ensuring a positive interaction despite any difficulties.
Types of Pleasant Agents
Pleasant agents can take various forms, each tailored to a specific purpose. Their function, while fundamentally similar, adapts to the context and complexity of the tasks they perform.
- Virtual Assistants: These agents handle tasks such as scheduling appointments, setting reminders, answering questions, and managing personal information. Their primary function is to simplify and streamline daily tasks for the user.
- Customer Service Representatives: These agents assist customers with inquiries, complaints, and resolving issues. They provide support and guidance in a manner that addresses customer concerns and resolves problems efficiently.
- Educational Assistants: These agents provide support and guidance in learning contexts, offering information, answering questions, and adapting to the individual needs of the learner. They are tailored to assist with academic or vocational tasks.
Comparison with Other Agents
Pleasant agents differ from other types of agents in their emphasis on positive user interaction. While other agents may focus solely on task completion, pleasant agents prioritize a positive emotional experience.
| Characteristic | Pleasant Agent | Other Agents (e.g., Task-Oriented Agents) |
|---|---|---|
| User Experience | Prioritizes positive emotional connection and a smooth, efficient process. | Focuses primarily on task completion, often without considering user emotions. |
| Communication Style | Empathetic, proactive, and concise. | Maybe personal or overly technical. |
| Problem Solving | Anticipates potential issues and proactively offers solutions. | Reacts to user requests and may not offer alternative solutions. |
Key Elements of a Positive User Experience
A positive user experience with a pleasant agent hinges on several key elements. These elements contribute to the overall satisfaction and efficiency of the interaction.
- Personalization: Tailoring the interaction to the individual user’s needs and preferences fosters a more meaningful and relevant experience.
- Accessibility: Ensuring the agent is available and responsive at the user’s convenience promotes user engagement.
- Adaptability: The agent’s ability to adjust to changing user needs and preferences throughout the interaction enhances its value and efficacy.
Agent Attributes and Behaviors
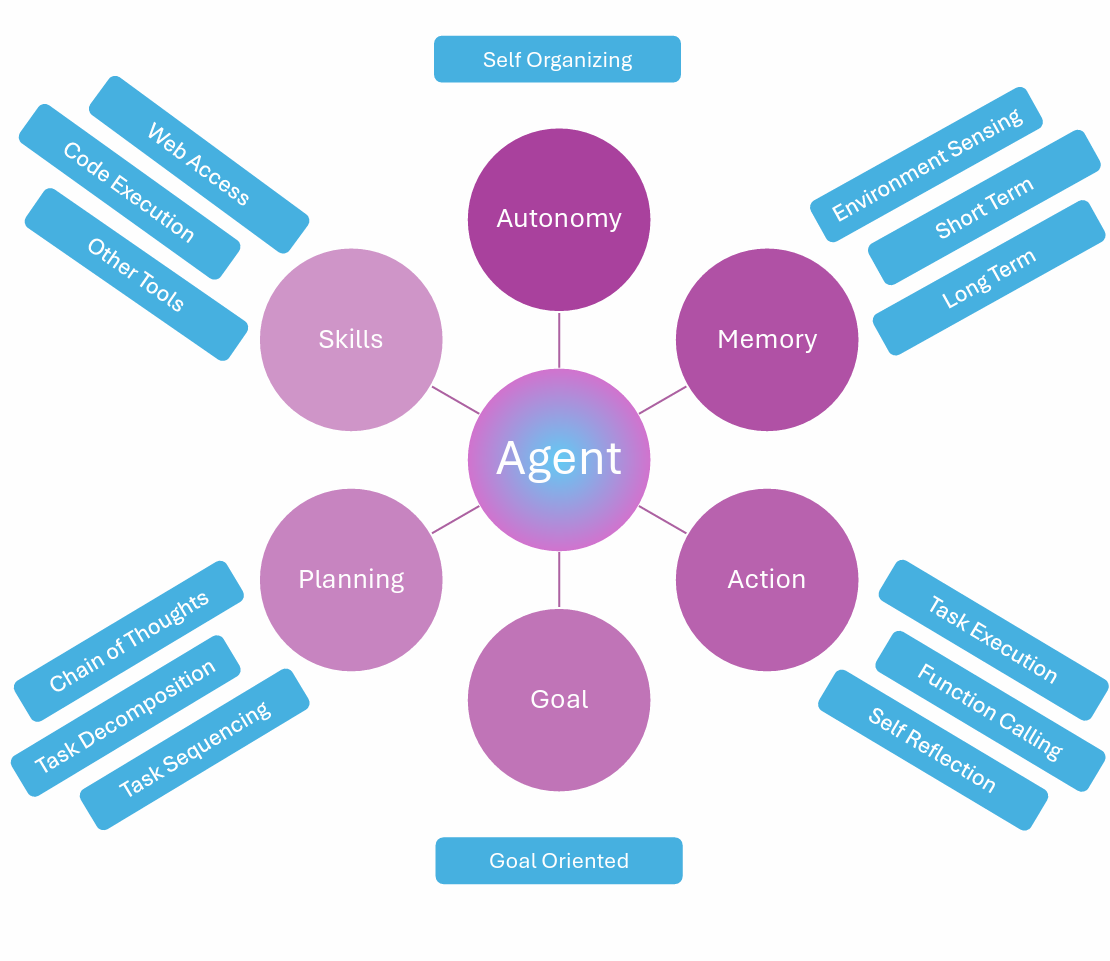
A pleasant agent fosters a positive user experience by demonstrating specific behaviors and attributes. This involves more than just politeness; it encompasses a range of interpersonal skills and a deep understanding of user needs. A pleasant agent should be proactive, anticipatory, and capable of adapting to individual user preferences.
Effective agent interactions are crucial for customer satisfaction and retention. Pleasant agents contribute significantly to building trust and positive brand perception. Their actions and communication styles directly influence the overall user experience.
Specific Behaviors of a Pleasant Agent
Pleasant agents consistently exhibit behaviors that contribute to a positive interaction. These behaviors include active listening, clear communication, and a proactive approach to problem-solving. Empathy and understanding play a key role in responding appropriately to user needs and concerns.
- Active Listening: Agents demonstrate active listening by paying close attention to the user’s words, tone, and nonverbal cues. This involves summarizing the user’s concerns and acknowledging their feelings, thereby ensuring that the user feels heard and understood.
- Clear Communication: Agents use clear, concise, and easily understandable language. They avoid jargon and technical terms whenever possible, ensuring the user can easily comprehend the information presented. This clarity enhances the user’s understanding and reduces frustration.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Agents anticipate potential issues and proactively address them before the user raises them. This proactive approach prevents escalation and fosters a positive user experience. An example would be suggesting alternative solutions if a primary option is unavailable.
- Empathy and Understanding: Agents demonstrate empathy by acknowledging the user’s emotions and concerns. This understanding allows the agent to tailor their response to better meet the user’s needs and reduce stress.
Tone of Voice and Language in Pleasant Agent Interactions
The tone of voice and language used by an agent significantly impact the user’s perception of pleasantness. A friendly, supportive, and encouraging tone fosters a positive interaction. Avoidance of negative language and aggressive or dismissive language is paramount.
- Friendly and Supportive Tone: A friendly and supportive tone helps create a sense of trust and comfort. This tone can be achieved through the use of positive language, such as “I can help you with that,” or “Let me see what I can do.” Examples include using terms like “please” and “thank you.”
- Clear and Concise Language: Using clear and concise language avoids ambiguity and misunderstandings. This clarity ensures the user comprehends the agent’s response and reduces the need for repeated clarification.
- Avoidance of Negative Language: Negative language, such as “Unfortunately or “I’m afraid,” can create a sense of negativity and frustration. Positive and constructive language should be prioritized. For example, using “Let’s try this alternative” instead of “This won’t work.”
Importance of Empathy and Understanding
Empathy and understanding are crucial for a pleasant agent interaction. Understanding the user’s perspective and acknowledging their feelings helps build rapport and resolve issues effectively. This fosters trust and a sense of collaboration between the agent and the user.
- Acknowledging User Feelings: Agents must acknowledge and validate the user’s emotions. For example, if a user expresses frustration, the agent should acknowledge that frustration and attempt to address it. This builds rapport and trust.
- Tailoring Responses to User Needs: Agents should tailor their responses to meet the specific needs of the user. This involves understanding the user’s context and providing relevant information. For instance, if a user is experiencing technical difficulties, the agent should offer specific solutions rather than general troubleshooting steps.
- Building Rapport: Building rapport through understanding fosters a sense of collaboration and trust between the agent and the user. Active listening and acknowledging the user’s emotions are essential for building rapport.
Effective Communication Strategies for a Pleasant Agent
Effective communication strategies are vital for a pleasant agent interaction. These strategies include active listening, clear communication, and the ability to adapt to the user’s needs and preferences.
- Active Listening: Active listening ensures that the user feels heard and understood. This involves not only hearing the words but also paying attention to the user’s nonverbal cues and emotions. This can lead to improved comprehension and successful resolution.
- Providing Clear and Concise Information: Providing clear and concise information helps the user understand the issue and possible solutions. This reduces ambiguity and improves the user experience.
- Adapting to User Needs and Preferences: Agents should adapt their communication style to suit the user’s needs and preferences. This might involve using different language, tone, or pace to ensure effective communication.
Agent Attributes and Their Impact on User Experience
| Attribute | Description | Impact on User |
|---|---|---|
| Empathy | Understanding and sharing the feelings of the user. | Builds trust and rapport, leading to a more positive interaction. |
| Patience | Ability to remain calm and composed during challenging situations. | Reduces frustration and anxiety, fostering a more positive experience. |
| Proactiveness | Anticipating user needs and taking initiative to address potential problems. | Enhances efficiency and satisfaction, leading to a smoother interaction. |
| Clear Communication | Presenting information straightforwardly and understandably. | Reduces misunderstandings and enhances user comprehension. |
| Problem-solving Skills | Ability to find effective solutions to user issues. | Increases user satisfaction by efficiently resolving problems. |
Interaction Design for Pleasant Agents
Designing pleasant interactions with agents is crucial for positive user experiences. A well-designed interaction framework considers the agent’s personality, the user’s needs, and the specific context of the interaction. This approach ensures that the agent is helpful, efficient, and enjoyable to interact with.
Effective interaction design goes beyond simple automation. It involves creating a conversational flow that feels natural and human-like, anticipating user needs and providing relevant information promptly. This requires careful consideration of communication styles, agent attributes, and the overall context of the interaction.
Interaction Framework
A robust framework for pleasant agent interactions considers several key elements. This includes defining clear interaction goals, selecting appropriate communication styles, and designing for seamless transitions between different interaction phases. The framework should also account for potential user errors and provide clear and concise guidance for resolution. This structure facilitates consistency and efficiency, leading to positive user experiences.
Examples of Pleasant Agent Interactions
Pleasant agent interactions are exemplified in various scenarios. In order processing, a pleasant agent might proactively offer alternative shipping options or provide real-time tracking updates. In customer support, a pleasant agent could empathize with the user’s issue, ask clarifying questions, and offer multiple resolution paths. These examples showcase how pleasant agents can go beyond basic task completion to enhance the overall user experience.
Best Practices for Pleasant Agent Interactions
Several best practices can guide the design of pleasant agent interactions. These include clear and concise communication, active listening, and the ability to adapt to diverse user needs. Employing empathy and offering helpful suggestions demonstrate a genuine desire to assist the user. These practices create a positive and productive interaction environment.
- Proactive Assistance: Anticipating user needs and offering helpful suggestions demonstrates a proactive approach, enhancing the user experience. This proactive assistance can include suggesting alternative solutions or providing relevant information before the user explicitly requests it.
- Personalized Communication: Tailoring interactions to individual user preferences and past interactions creates a more personalized and engaging experience. This could involve using previously collected user data to offer tailored recommendations or solutions.
- Clear and Concise Language: Using simple, easily understandable language avoids ambiguity and ensures the user comprehends the information. This includes avoiding technical jargon or overly complex sentence structures.
- Empathetic Responses: Acknowledging and validating user emotions, especially in challenging situations, fosters a sense of connection and trust. This empathy can be demonstrated through empathetic language and acknowledgement of the user’s frustration.
Communication Styles for Pleasant Interactions: Pleasant agent different communication styles can be leveraged to create pleasant interactions. A friendly and helpful tone is often effective, while maintaining professionalism is crucial. Empathetic responses, tailored to the specific context, can also enhance the user experience. Adaptability in communication styles allows agents to effectively address diverse user needs.
- Formal Communication: Formal communication is essential in professional settings, maintaining a professional tone and avoiding casual language. This approach ensures clarity and precision in the interaction.
- Informal Communication: In some situations, an informal communication style can foster a more relaxed and friendly atmosphere, especially when dealing with routine or straightforward requests. This approach can be effective in building rapport.
- Empathetic Communication: Understanding and acknowledging user emotions is vital in situations involving frustration or difficulty. Empathetic communication validates users’ feelings and demonstrates a genuine desire to assist.
Interaction Design Elements for Agent Types
The table below shows the key interaction design elements for various agent types.
| Agent Type | Interaction Goal | Communication Style | Example Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Order Processing Agent | Confirm order details, provide updates, handle adjustments | Friendly, informative, proactive | “Thank you for your order! We’ve received it and are processing it now. We’ll send you a confirmation email shortly, and you can track your package here…” |
| Customer Support Agent | Resolve customer issues, provide solutions, build trust | Empathetic, problem-solving, patient | “I understand your frustration. Let’s take a look at the issue. Can you describe what happened?” |
| Sales Agent | Convert leads to customers, close deals | Enthusiastic, persuasive, helpful | “Based on your needs, I recommend the X product. It comes with a 1-year warranty and has great reviews.” |
Pleasant Agent Training and Development
Cultivating pleasant agents requires a structured approach to training and development. This involves not just teaching the technical skills of interaction but also fostering the soft skills that contribute to a positive user experience. A well-designed training program will equip agents with the knowledge and tools necessary to consistently deliver a pleasant interaction.
Effective training programs for pleasant agents are essential for maintaining a high standard of service. These programs must be designed to equip agents with the necessary knowledge, skills, and behaviors to consistently create a positive user experience. A well-structured approach, coupled with ongoing feedback, will ensure that pleasant agent performance is not only achieved but also maintained.
Methods for Training Agents to be Pleasant
Training pleasant agents requires a multifaceted approach that combines theoretical instruction, practical exercises, and real-world scenarios. Role-playing, simulations, and feedback mechanisms are crucial for fostering the desired behaviors.
- Active Listening Techniques: Training should emphasize active listening, including verbal and nonverbal cues. Agents need to learn to understand not only what is being said but also the underlying emotions and needs of the user. This might involve practicing techniques like paraphrasing and reflecting what the user has said to ensure understanding.
- Empathy and Emotional Intelligence: Training programs should explicitly address the importance of empathy and emotional intelligence. Agents need to be able to understand and respond to the emotional state of the user, whether positive or negative. This might involve case studies of different user emotional states and how to respond appropriately.
- Positive Communication Skills: Agents must be equipped with positive communication skills, including clear and concise language, appropriate tone of voice, and respectful language. These skills should be explicitly taught, practiced, and reinforced during the training process. Examples of positive communication could include using encouraging language and reframing negative feedback in a positive light.
- Conflict Resolution Techniques: Agents need to be equipped to handle difficult situations and conflicts with users calmly and professionally. This could include role-playing scenarios involving escalated interactions and practicing techniques to de-escalate the situation.
Importance of Consistent Training for Pleasant Agent Performance
Consistent training is crucial for maintaining the desired level of pleasantness in agents. New information and best practices are constantly evolving, so ongoing reinforcement and updates are essential.
Continuous training prevents agents from becoming stagnant in their approach. It helps them adapt to changing user expectations and industry standards. A lack of consistent training could lead to a decline in agent performance and a negative user experience.
Elements of a Comprehensive Training Program for Pleasant Agents
A comprehensive training program for pleasant agents should encompass various aspects, including theoretical knowledge, practical application, and ongoing feedback mechanisms. Regular assessments and reinforcement of learned skills are also crucial.
- Theoretical Modules: The program should include theoretical modules on customer service principles, communication styles, and emotional intelligence. This could include studying different communication styles and their effectiveness in various scenarios.
- Practical Exercises: Role-playing exercises and simulations are essential for the practical application of learned skills in a safe environment. These exercises should replicate real-world scenarios to enhance agents’ ability to handle different situations.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Regular feedback from supervisors, users, and colleagues is essential for identifying areas for improvement and reinforcing positive behaviors. This feedback should be constructive and actionable. Methods for gathering feedback might include surveys, performance reviews, and user reviews.
- Ongoing Reinforcement: Training should not be a one-time event. Regular workshops, refresher courses, and updates on best practices are essential for maintaining the desired level of pleasantness.
Role of Feedback in Improving Agent Pleasantness
Feedback is a critical component in improving agent pleasantness. It provides valuable insights into areas that need improvement and helps agents refine their approach to user interactions.
Constructive feedback should be specific and actionable. Instead of simply stating that an interaction was “bad”, the feedback should identify specific behaviors or language that could be improved. This helps agents understand the impact of their actions on users.
Different Training Techniques that Can Improve the Pleasantness of Agents
Various techniques can be used to enhance the pleasantness of agents. These techniques should focus on developing soft skills and improving communication abilities.
- Mentorship Programs: Experienced pleasant agents can mentor new agents, guiding them through challenging interactions and providing valuable insights. This provides an opportunity for knowledge transfer and practical guidance.
- Interactive Simulations: Interactive simulations can recreate real-world scenarios, allowing agents to practice handling difficult situations in a controlled environment. This can help agents develop confidence and refine their problem-solving skills in a risk-free setting.
- Gamification: Incorporating elements of gamification, like points and badges, can incentivize agents to engage in training and improve their pleasantness. This can make the training process more engaging and enjoyable.
Measuring Pleasantness
Assessing the pleasantness of an agent’s performance is crucial for improving user experience and achieving desired outcomes. A well-defined methodology for measuring pleasantness allows for consistent evaluation and facilitates continuous improvement in agent training and development. This section, Artikels a practical approach to quantify pleasant interactions, considering key factors and user feedback.
Methods for Evaluating Agent Pleasantness
Quantifying agent pleasantness requires a multi-faceted approach. Subjective user experiences, combined with measurable metrics, provide a comprehensive evaluation. This involves understanding the nuances of user interaction and translating them into quantifiable data points.
Factors to Consider in Evaluating Pleasantness
Several key factors influence a user’s perception of an agent’s pleasantness. These include the agent’s communication style, empathy, responsiveness, and problem-solving abilities. A helpful agent will exhibit patience, active listening, and a clear understanding of the user’s needs. Additionally, the agent’s ability to maintain a professional and courteous demeanor throughout the interaction contributes significantly to the overall pleasantness.
Metrics for Quantifying Pleasant Agent Interactions
A range of metrics can be used to measure agent performance and assess the pleasantness of interactions. These metrics provide a structured framework for evaluating various aspects of the interaction.
| Metric | Description | How to Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Agent Response Time | The time taken by the agent to respond to user queries. | Measure the time elapsed between the user’s input and the agent’s response. Average response time over a set number of interactions is a useful metric. |
| User Satisfaction Score (USS) | A numerical rating reflecting the user’s overall satisfaction with the interaction. | Employ a standardized satisfaction survey at the end of the interaction, allowing users to rate their experience on a scale (e.g., 1-5 stars). Calculate the average USS across a sample of interactions. |
| Problem Resolution Rate | The percentage of interactions where the agent successfully resolved the user’s problem. | Track the number of successful resolutions and divide it by the total number of interactions. |
| Empathy Score | The perceived degree of empathy displayed by the agent. | Use a pre-defined scale (e.g., 1-5) to rate the agent’s ability to understand and acknowledge the user’s emotions and needs during the interaction. Average the scores across multiple interactions. |
| Agent Tone and Language | The tone and language used by the agent to communicate with the user. | Evaluate the agent’s tone (e.g., friendly, professional) and language (e.g., clear, concise) through a standardized rubric. Assign scores to different aspects of the communication. |
| Active Listening | The degree to which the agent demonstrates active listening during the interaction. | Assess the agent’s responses, observing if they demonstrate understanding and acknowledgement of the user’s points. Use a rubric to evaluate the agent’s attentiveness. |
Analyzing User Feedback to Assess Agent Pleasantness
User feedback provides invaluable insights into the agent’s performance and helps to identify areas for improvement. This feedback can be gathered through various channels, including surveys, feedback forms, and direct comments. Qualitative analysis of the feedback is critical in identifying patterns and trends in user experiences.
“Analyzing user feedback allows for a nuanced understanding of the user experience, going beyond simple numerical scores and providing context to agent performance.”
Analyzing user feedback involves reading through comments and identifying recurring themes or issues. For instance, if users repeatedly mention the agent’s tone as being unhelpful or abrupt, it signals a potential area for training or adjustment in communication protocols.
Pleasant Agent in Different Contexts
Pleasant agents, designed for positive interactions, can enhance various applications beyond basic customer service. Their ability to adapt to diverse situations and maintain a positive demeanor makes them valuable assets across multiple sectors. Their application requires careful consideration of context-specific challenges and opportunities.
Customer Service Applications
Pleasant agents excel in customer service by providing a supportive and empathetic experience. This approach can significantly improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. By maintaining a calm and reassuring tone, they can resolve issues efficiently and effectively. Furthermore, their proactive nature can help prevent problems from escalating.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: A pleasant agent’s focus on positive interactions and problem-solving can lead to a marked increase in customer satisfaction ratings. This translates to higher customer retention and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
- Improved Issue Resolution: Their ability to listen actively and empathize can help them understand customer concerns more effectively, leading to quicker and more satisfactory resolution of issues.
- Proactive Problem Prevention: By anticipating potential problems and offering solutions, pleasant agents can proactively address concerns before they escalate into major issues, thereby reducing customer frustration.
Entertainment Applications
Pleasant agents can add a layer of engagement and personalization to entertainment experiences. For example, in online gaming, a pleasant agent could provide tailored recommendations or assistance without feeling intrusive. In virtual reality environments, they could guide users through new experiences helpfully and enjoyably.
- Personalized Recommendations: In gaming, a pleasant agent can offer customized suggestions for activities, characters, or items based on the user’s play style and preferences, enhancing the gaming experience.
- Interactive Storytelling: In virtual reality or interactive story experiences, a pleasant agent can guide the user through different narrative paths positively and encouragingly, making the experience more enjoyable.
- Virtual Assistants: In virtual environments, pleasant agents can serve as helpful assistants, providing information, answering questions, and guiding users through various aspects of the virtual world.
Educational Applications
Pleasant agents can personalize the learning experience for students by providing immediate feedback and support. They can also create a more engaging and supportive learning environment.
- Personalized Learning Paths: A pleasant agent can adapt learning materials and activities to suit each student’s individual needs and pace, optimizing the learning process.
- Immediate Feedback: Pleasant agents can provide instant feedback on assignments and exercises, allowing students to learn and improve more effectively.
- Supportive Learning Environment: Their positive demeanor and proactive approach can foster a supportive and encouraging learning environment for all students.
Challenges and Opportunities Across Industries
The implementation of pleasant agents across industries presents unique challenges and opportunities. One significant challenge is maintaining consistency in the agent’s personality and behavior across different contexts. Another is ensuring the agent’s responses remain relevant and appropriate to the specific situation. However, the potential benefits are substantial, including improved customer satisfaction, increased efficiency, and enhanced user engagement.
| Industry | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Service | Maintaining consistency across diverse customer profiles and issues. | Increased customer satisfaction and reduced resolution times. |
| Entertainment | Ensuring the agent’s personality aligns with the specific game or experience. | Enhanced player engagement and personalization. |
| Education | Adapting to the dynamic needs of individual learners. | Personalized learning and improved student support. |
“A pleasant agent, interacting with a customer experiencing technical difficulties with their online banking platform, could calmly guide them through troubleshooting steps, using a reassuring tone and positive language to ensure the customer feels supported throughout the process.”
Future of Pleasant Agents
The future of pleasant agents promises a significant evolution in human- computer interaction, driven by advancements in AI and machine learning. These agents will increasingly adapt to individual user preferences, fostering more natural and empathetic interactions. This evolution will reshape customer service, personal assistance, and even creative endeavors.
Potential Future Trends
The development of pleasant agents will be marked by several key trends. These trends include an enhanced capacity for emotional intelligence, enabling agents to better understand and respond to human emotions. Furthermore, agents will become more adept at personalizing interactions, anticipating user needs, and offering proactive assistance. This personalized approach will make interactions feel more tailored and less robotic. Finally, agents will likely incorporate more advanced natural language processing, allowing for more fluid and intuitive communication.
AI and Machine Learning’s Role
AI and machine learning are instrumental in shaping the future of pleasant agents. Sophisticated algorithms will analyze vast amounts of data to understand user behavior, preferences, and emotional states. This data-driven approach will enable agents to adapt their responses and interactions in real time, leading to more personalized and satisfying experiences. Furthermore, machine learning models will enable agents to learn from past interactions, improving their performance and efficiency over time. For instance, a pleasant agent assisting with online shopping could learn from user feedback to suggest more relevant products and tailor the purchasing experience to the individual user.
Innovative Approaches
Several innovative approaches are emerging in the creation of pleasant agents. One approach involves incorporating elements of human psychology into the design of agent interactions. This approach aims to create more natural and empathetic interactions by incorporating principles of communication and social interaction. Another approach focuses on developing agents that can learn and adapt from diverse sources of data, including text, audio, and video. These approaches enable agents to develop a comprehensive understanding of user behavior and context, thereby leading to more appropriate and satisfying responses. For example, a virtual assistant used for scheduling could incorporate information from user calendars and emails to anticipate and proactively address potential scheduling conflicts.
Evolution of Interactions
The evolution of pleasant agent interactions will be marked by a shift from simple, rule-based responses to more complex, nuanced interactions. Future agents will be able to understand context, respond to emotional cues, and engage in more dynamic and fluid conversations. This evolution is closely tied to advancements in natural language processing and the increasing capacity of agents to understand complex language structures and nuances. For example, a pleasant agent handling customer support could recognize subtle indicators of frustration in a customer’s tone of voice and adjust their response accordingly, potentially offering alternative solutions or empathetic support.
Ethical Considerations
The development and use of pleasant agents raise important ethical considerations. Ensuring fairness and transparency in agent interactions is crucial to prevent biases and ensure equitable outcomes for all users. Furthermore, the potential for agents to manipulate or mislead users must be carefully addressed through robust ethical guidelines and regulations. Ultimately, the responsible development and deployment of pleasant agents are essential to ensure their positive impact on society. For example, guidelines could be established to prevent agents from perpetuating harmful stereotypes or making inaccurate claims.
End of Discussion

Source: blogspot.com
In conclusion, crafting a pleasant agent requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on user needs and expectations. By understanding the essential characteristics, behaviors, and interaction design principles, developers can create agents that provide positive and effective experiences across various contexts. This detailed exploration of pleasant agents emphasizes the importance of a user-centric design philosophy, laying the foundation for future innovations in this evolving field. The future holds exciting possibilities for the application of these principles in an expanding range of applications.